The Gila and Salt River Meridian, a defining geographic feature of Arizona, has played a pivotal role in shaping the state’s boundaries, land ownership, and cultural heritage. Its establishment in the 19th century set the stage for the development of Arizona’s cities, towns, and infrastructure, leaving an enduring legacy that continues to impact the state’s landscape and communities.
From its historical origins to its contemporary relevance, the Gila and Salt River Meridian offers a fascinating glimpse into Arizona’s past, present, and future.
Historical Background

The Gila and Salt River Meridian was established in 1851 to serve as the principal meridian for the public land surveys in the Arizona Territory. The meridian is a north-south line that runs through the center of the territory, and it is used to divide the land into townships and sections.The
establishment of the Gila and Salt River Meridian was a significant event in the history of Arizona. It allowed for the orderly settlement of the territory and the development of its natural resources. The meridian has also played an important role in the development of Arizona’s transportation and communication systems.
Timeline of Significant Events
* 1851: The Gila and Salt River Meridian is established.
1863
The Arizona Territory is created.
1864
The first township is surveyed in the Arizona Territory.
1880
The last township is surveyed in the Arizona Territory.
1912
Arizona becomes a state.
Historical Documents and Maps
The following historical documents and maps illustrate the development of the Gila and Salt River Meridian:* The original survey plat of the Gila and Salt River Meridian (1851)
- A map of the Arizona Territory showing the Gila and Salt River Meridian (1864)
- A map of Arizona showing the townships and sections surveyed by the Gila and Salt River Meridian (1880)
Geographic Significance
The Gila and Salt River Meridian (GSRM) is a north-south line established in 1851 to serve as the principal meridian for Arizona Territory. It runs through the heart of the state, from the Utah border in the north to the Mexican border in the south.
The GSRM plays a crucial role in defining boundaries and land ownership in Arizona. It divides the state into two halves: the Eastern and Western halves. All land surveys in Arizona are based on the GSRM, and property descriptions often refer to it as a reference point.
Examples of the GSRM’s Influence on Arizona’s Geography
- The GSRM forms the boundary between the counties of Maricopa and Pinal.
- The meridian also defines the eastern boundary of the Tohono O’odham Indian Reservation.
- Many roads and highways in Arizona are aligned with the GSRM, including Interstate 10 and State Route 87.
Surveying and Mapping

The establishment of the Gila and Salt River Meridian required precise surveying and mapping techniques. Surveyors employed a combination of traditional and innovative methods to create an accurate and reliable grid system.
Surveying Techniques
- Chain and Compass:Surveyors used a Gunter’s chain, a 66-foot measuring device, to measure distances. The compass provided direction, allowing surveyors to establish straight lines.
- Solar Observations:To determine latitude and longitude, surveyors made astronomical observations using a sextant and a chronometer. These observations were essential for accurately orienting the meridian.
- Triangulation:Surveyors established a series of triangulation stations, using theodolite instruments to measure angles and calculate distances. This technique allowed them to create a precise network of reference points.
Challenges Faced by Surveyors
Surveyors encountered numerous challenges in the field, including:
- Rugged Terrain:The mountainous and desert landscape of Arizona presented obstacles to traversing and measuring distances.
- Extreme Temperatures:The scorching heat and freezing cold of the region made it difficult for surveyors to work for extended periods.
- Hostile Native American Tribes:Surveyors had to be cautious of Native American tribes who were often wary of the government’s presence.
Historical Accounts
One notable account of the surveying process involves Edward F. Beale, a surveyor who established the 11th Standard Parallel South in 1857. Beale’s party faced numerous challenges, including a lack of water, hostile Native Americans, and difficult terrain. Despite these obstacles, they successfully completed their mission, providing a critical reference line for the Gila and Salt River Meridian.
Impact on Land Development
The Gila and Salt River Meridian played a pivotal role in shaping the development of Arizona’s landscape. It established a standardized grid system that guided the distribution of land parcels and infrastructure, thereby influencing the location and growth of cities, towns, and transportation networks.
Cities and Towns
The meridian’s lines determined the placement of settlements throughout Arizona. Cities like Phoenix, Scottsdale, and Mesa emerged at the intersections of major grid lines, where access to transportation and resources was optimal. These urban centers became hubs of commerce, industry, and population growth.
The Gila and Salt River Meridian is a key reference point for land surveys in the southwestern United States. To test your knowledge about this and other Battlestar Galactica-related topics, check out the BSG Quiz 2 Answers 2019 . After brushing up on your BSG trivia, you can return to exploring the history and significance of the Gila and Salt River Meridian.
Infrastructure
The meridian also influenced the development of infrastructure, including roads, railroads, and canals. Transportation routes followed the grid lines, connecting settlements and facilitating the movement of goods and people. Canals, such as the Salt River Project, were built along the meridian’s lines to irrigate agricultural lands and support the region’s economic development.
Economic and Social Implications
The meridian’s impact on land development had significant economic and social implications. It facilitated the orderly distribution of land parcels, reducing conflicts and disputes. It also enabled efficient planning and development, leading to a more organized and prosperous society. The grid system provided a framework for land ownership, taxation, and resource management, fostering economic stability and growth.
Legal and Administrative Uses: Gila And Salt River Meridian

The Gila and Salt River Meridian holds significant legal and administrative importance, serving as a pivotal reference point in boundary disputes, land ownership disputes, and property descriptions.
In boundary disputes, the meridian acts as an impartial guide, providing a clear and established line of demarcation between adjacent properties or jurisdictions. This helps prevent conflicts and ensures accurate and fair land division.
Land Ownership Disputes
In land ownership disputes, the Gila and Salt River Meridian plays a crucial role in determining the rightful owners of contested parcels. By referencing the meridian’s precise coordinates, surveyors can accurately establish property boundaries and resolve disputes based on legal land descriptions.
Property Descriptions
The meridian is also integral to property descriptions in legal documents, such as deeds and surveys. By referencing the meridian and its corresponding townships and ranges, property descriptions provide a precise and unambiguous identification of the location and boundaries of the property in question.
Cultural and Historical Significance
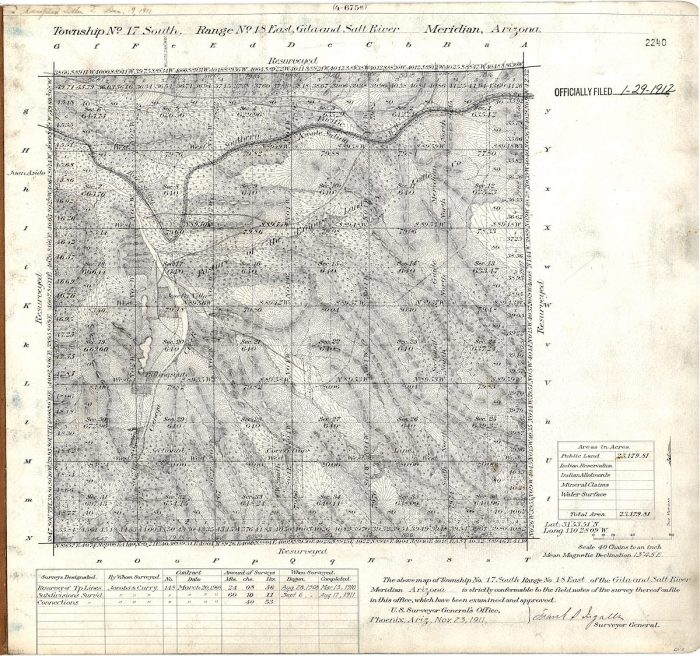
The Gila and Salt River Meridian is not just a geographic line; it holds profound cultural and historical significance for Arizona and the Southwest. It serves as a testament to the region’s rich past, shaping its identity and contributing to its unique character.
As the boundary between eastern and western Arizona, the meridian played a pivotal role in the development of the territory. It guided settlers, explorers, and land surveyors, marking the division between different cultural and economic zones. The eastern portion, with its abundant water resources, attracted agricultural communities, while the western region became a hub for mining and ranching.
Stories and Anecdotes
- Legend has it that the meridian was first surveyed by a group of cowboys who used a long rope to measure the distance between the Gila and Salt Rivers. The rope was marked with knots at regular intervals, and the cowboys would ride along the rope, counting the knots to determine the distance.
- In the early 1900s, the meridian was used as a dividing line between the Navajo and Hopi reservations. This division had a significant impact on the lives of both tribes, as it separated their traditional lands and disrupted their cultural practices.
- Today, the meridian continues to serve as a cultural landmark. It is often used as a reference point for hikers, campers, and other outdoor enthusiasts who explore the region.
Contemporary Relevance

The Gila and Salt River Meridian remains an indispensable tool in modern surveying, mapping, and land management in Arizona. It provides a consistent and accurate reference point for determining property boundaries, planning infrastructure projects, and managing natural resources.
Use in Modern Surveying and Mapping, Gila and salt river meridian
The meridian serves as a baseline for establishing land surveys and creating maps. Surveyors use the meridian to determine the precise location of property corners, easements, and other land features. This information is essential for creating accurate property descriptions, resolving boundary disputes, and ensuring the orderly development of land.
Land Management and Planning
The meridian is also crucial for land management and planning purposes. It helps agencies such as the Bureau of Land Management and the Arizona State Land Department to manage public lands, allocate resources, and plan for future development. The meridian provides a common reference point for coordinating land use planning and ensuring compatibility between different land uses.
Shaping Arizona’s Landscape and Communities
The Gila and Salt River Meridian has played a significant role in shaping Arizona’s landscape and communities. It has guided the establishment of towns, cities, and transportation networks. The meridian has also influenced the distribution of agriculture, mining, and other economic activities.
By providing a reliable and consistent reference point, the meridian has helped to create a more orderly and efficient land use system in Arizona.
Common Queries
What is the Gila and Salt River Meridian?
The Gila and Salt River Meridian is a north-south line that serves as the principal meridian for Arizona. It was established in 1851 to provide a reference point for surveying and mapping the state.
How did the Gila and Salt River Meridian impact Arizona’s development?
The meridian played a crucial role in defining Arizona’s boundaries, determining the location of cities and towns, and facilitating land ownership. It also influenced the state’s economic and social development.
What is the cultural significance of the Gila and Salt River Meridian?
The meridian has become a symbol of Arizona’s history and identity. It is often referenced in literature, art, and music, and is a popular destination for tourists and historians.