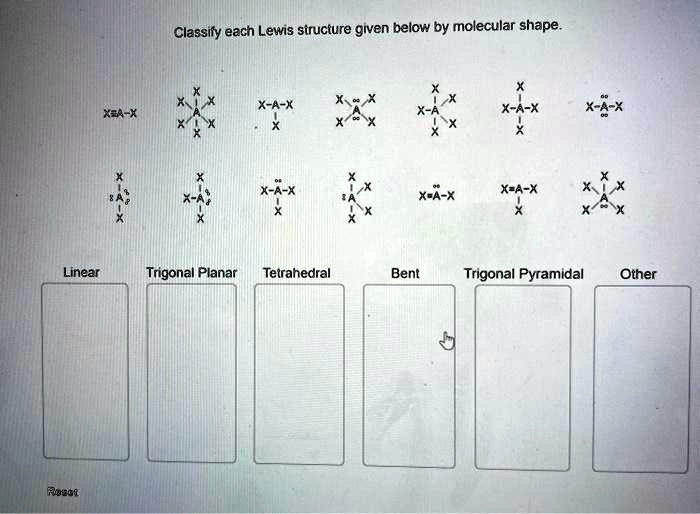
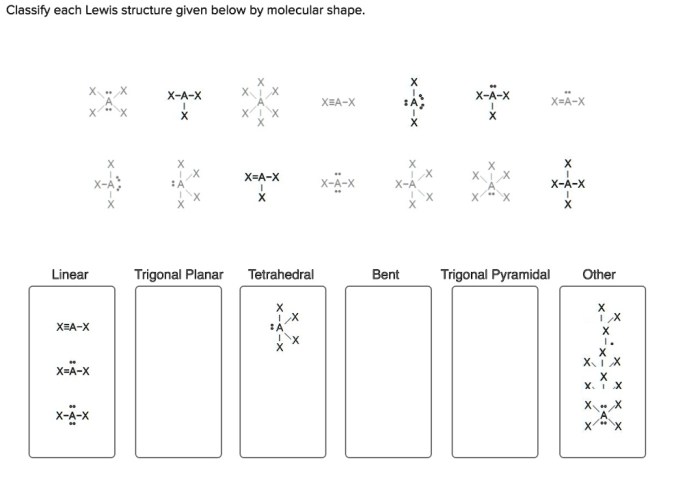
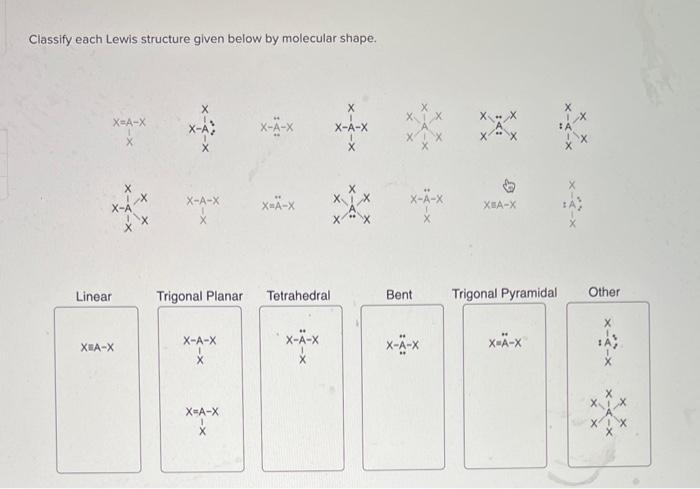
Classify each lewis structure given below by molecular shape. – As the topic of classifying Lewis structures by molecular shape takes center stage, this introductory paragraph invites readers into a realm of chemistry, where molecular shapes play a pivotal role in understanding the behavior and properties of molecules. This discourse promises to unveil the intricacies of molecular geometry, empowering readers with a deeper comprehension of the chemical world.
Molecular shape, a fundamental aspect of chemistry, governs the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, influencing its reactivity, polarity, and other crucial properties. Understanding molecular shapes is essential for deciphering the behavior of molecules in various chemical processes and applications.
Molecular Shape
Molecular shape refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is determined by the number and type of atoms present, as well as the bonding between them. Molecular shape is crucial in chemistry as it influences various properties of a molecule, including its reactivity, polarity, and physical state.
Types of Molecular Shapes
- Linear:Molecules with two atoms bonded together in a straight line.
- Bent:Molecules with three atoms bonded together, forming a V-shape.
- Trigonal planar:Molecules with three atoms bonded to a central atom, forming a flat triangle.
- Tetrahedral:Molecules with four atoms bonded to a central atom, forming a three-dimensional tetrahedron.
VSEPR Theory
The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used to predict the molecular shape based on the number of valence electron pairs around the central atom. The theory states that electron pairs repel each other and will adopt an arrangement that minimizes this repulsion.
Lewis Structures, Classify each lewis structure given below by molecular shape.
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the bonding between atoms in a molecule. They show the valence electrons as dots and the chemical bonds as lines. Lewis structures can be used to determine the molecular shape by counting the number of electron pairs around the central atom.
Classifying Lewis Structures
| Molecular Shape | Lewis Structure Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Linear | Two electron pairs around the central atom |
| Bent | Three electron pairs around the central atom |
| Trigonal planar | Three electron pairs around the central atom, with no lone pairs |
| Tetrahedral | Four electron pairs around the central atom |
Examples
CH4: Tetrahedral shape, four electron pairs around the central carbon atom.
NH3: Trigonal planar shape, three electron pairs around the central nitrogen atom.
H2O: Bent shape, two electron pairs around the central oxygen atom.
CO2: Linear shape, two electron pairs around the central carbon atom.
Exceptions and Limitations
VSEPR theory and Lewis structures are generally accurate in predicting molecular shapes. However, there are some exceptions and limitations, such as:
- Molecules with lone pairs on the central atom may have distorted shapes.
- Molecules with resonance structures may have multiple possible shapes.
- Large molecules with complex structures may not conform to VSEPR theory.
FAQ Overview: Classify Each Lewis Structure Given Below By Molecular Shape.
What is the significance of molecular shape in chemistry?
Molecular shape plays a crucial role in determining a molecule’s physical and chemical properties, including its reactivity, polarity, and intermolecular interactions. It influences the molecule’s ability to participate in chemical reactions, form crystals, and interact with other molecules.
How does VSEPR theory help in predicting molecular shapes?
VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory provides a conceptual framework for understanding and predicting molecular shapes. It postulates that electron pairs around a central atom repel each other, leading to specific arrangements that minimize repulsion and determine the molecular geometry.
What are the limitations of using VSEPR theory to predict molecular shapes?
VSEPR theory is a simplified model that assumes electron pairs are localized and behave as point charges. It may not accurately predict the shapes of molecules with complex electronic structures, such as those involving resonance or hyperconjugation.